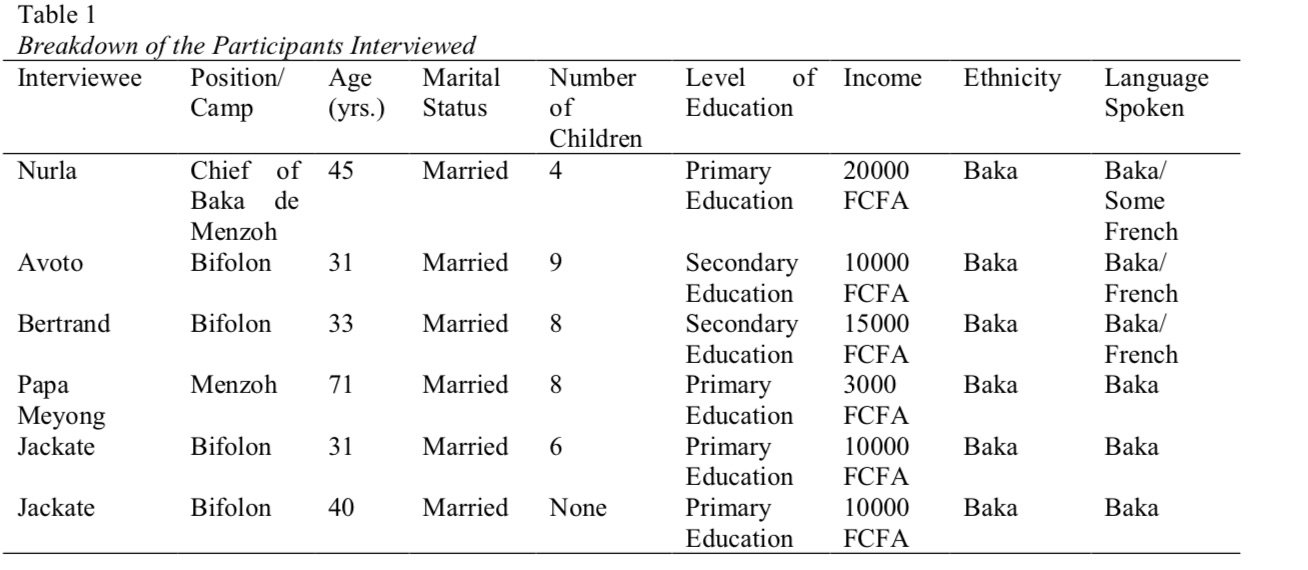
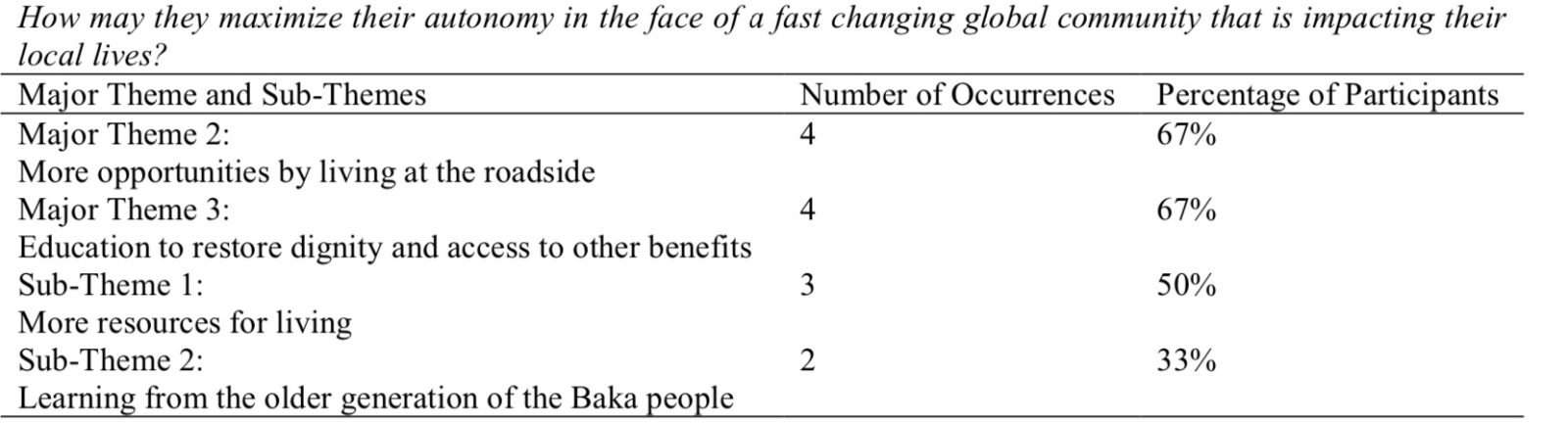
Bonecas da Prosperidade
RESUMO: BONECA AFRICANA DA ETNIA NDAMJI, DO NORTE DE CAMARÕES. PEÇA USADA PARA PROSPERIDADE E FERTILIDADE DAS FAMILIAS NDAMJI. ESCULTURA ATUAl.
Na África, as bonecas são de grande significado cultural. Além de suas aparências distintas, as bonecas têm diversas funções. Elas são usadas como amuletos de boa sorte e amuletos, decorações, presentes, brincadeiras, práticas rituais e heranças de família. Bonecas são feitas de praticamente qualquer coisa; argila, madeira e fibra tecida.
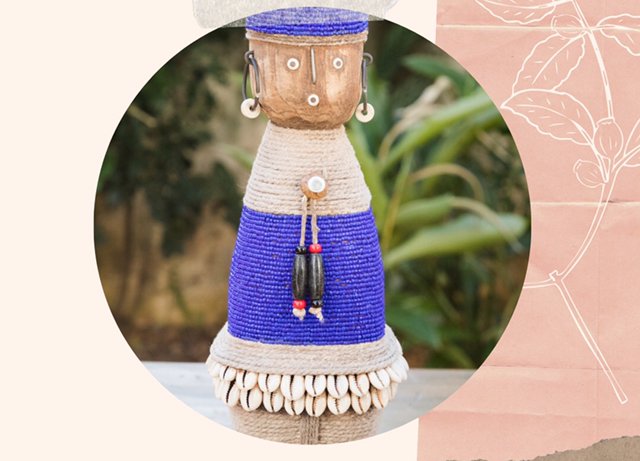
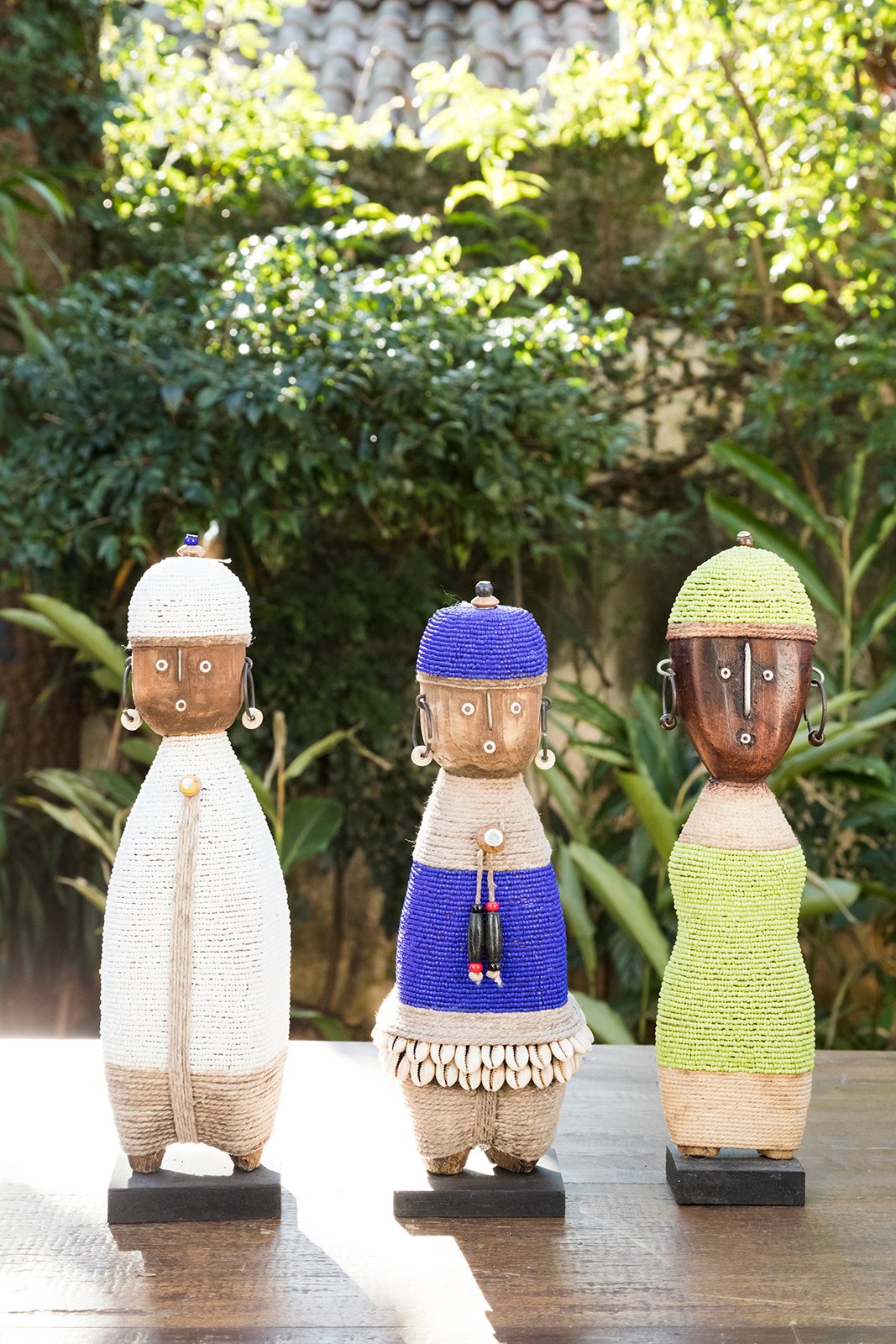
As Bonecas Namji, também conhecidas como Bonecas Dowayo, são bonecas de fertilidade e prosperidade nativas da tribo Namji, no norte dos Camarões, comuns da década de 1940.
Elas são esculpidas em Pau-rosa Africano, uma leguminosa nativa da República Democrática do Congo, Camarões, Gabão e Guiné Equatorial. Um único bloco de madeira de jacarandá africano é esculpido à mão em forma geométrica e decorado com miçangas coloridas, metais, fibra, conchas de búzios, moedas e até mesmo couro. Cada boneca é esculpida com uma estatura única e expressão facial.
Elas tem diferentes formas geométricas. Algumas são curtas, outras longas e esguios, outras gordas, outros finas. As bonecas são marrons, com uma cabeça redonda grande, com olhos esboçados, nariz e boca que lhes dá uma expressão facial cômica, em posição típica rígida e vertical. Seu corpo é coberto com tecido de contas multicoloridas e pérolas de vidro, as mãos e os pés são decorados com correntes de conchas de búzios. As vezes moedas coloniais são anexadas aos ombros, braços e pernas usando pérolas de vidro. Embora a maioria das bonecas sejam femininas, também existem versões masculinas.

Tradição e Uso
Bonecas Namji são amuletos de fertilidade e prosperidade dadas aos casais durante uma cerimônia de casamento. Os Namji acreditam que estes bonecos são feitos com poderosos encantos que aumentam a fertilidade da noiva, afastam os maus espíritos que causam infertilidade e trabalho de parto difícil. Além disso, elas simbolizam prosperidade para o casal, para a vida nova e para as novas empreitadas.
Muitas vezes a noiva carrega a boneca como um amuleto de boa sorte em qualquer lugar que ela vá, em sua bolsa ou roupa. Uma vez que o casal tem um filho, a boneca é colocada no altar da família ou passada para o bebê.
Bonecas Namji também são dadas às crianças para elas brincarem, quem tratam as bonecas como seus bebês: alimentado-as, banhando-nas, vestindo-las, etc. As crianças podem brincar com essas bonecas até a puberdade. Acredita-se que tais dramatizações incentivem as meninas a se prepararem para seus futuros papéis como mães.
Por causa de sua autenticidade e herança cultural, as Bonecas Namji são consideradas as bonecas mais bonitas da África.